The ABCs of Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease
What to look for in your radiographic study
|
|
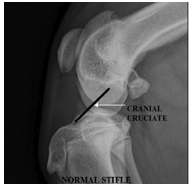 Normal Stifle No evidence of joint effusion No evidence of bone reaction where the cranial cruciate inserts into the proximal cranial surface of the tibia. |
|
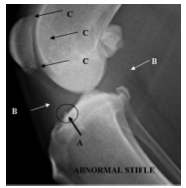 Abnormal Stifle A. Osseous reaction where cruciate inserts into the tibia. B. Increased soft tissue volume in the joint. C. Multicentric areas of new bone production and loss. Even if there is no joint laxity, if there is reaction where the cruciate inserts into the proximal tibia, then the cruciate ligament is involved in the disease process. |
